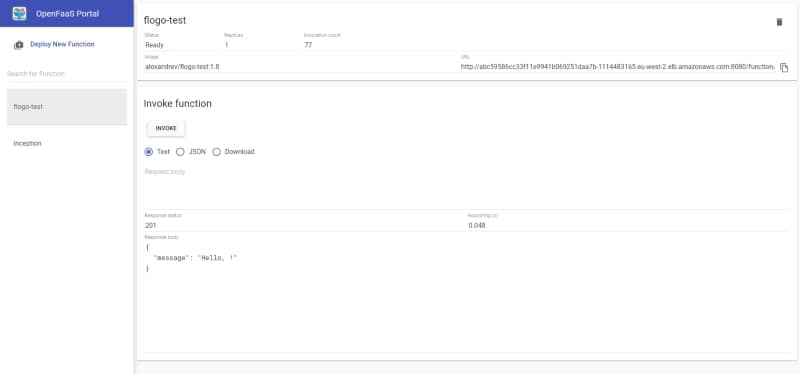
Bringing the Serverless Experience To Your Kubernetes Cluster
Serverless always has been considered the next step in the cloud journey. You know what I mean: you start from your VM on-premises, then you move to have containers on a PaaS platform, and then you try to find your next stop in this journey that is serverless.
Serverless is the idea of forgetting about infrastructure and focusing only on your apps. There is no need to worry about where it will run or the management of the underlying infrastructure. Serverless has started as a synonym of the Function as a Service (FaaS) paradigm. It has been populated first by the Amazon Lambda functions and later by all the major cloud providers.
It started as an alternative to the containerized approach that probably requires a lot of technical skills to manage and run at a production scale, but this is not the case anymore.
We have seen how the serverless approach has reached any platform despite this starting point. Following the same principles, we have different platforms that its focus is to abstract all technical aspects for the operational part and provide a platform where you can put your logic running. Pretty much every SaaS platform covers this approach but I would like to highlight some samples to clarify:
- netlify is a platform that allows you to deploy your web application without needing to manage anything else that the code needed to run it.
- TIBCO Cloud Integration is an iPaaS solution that provides all the technical resources you could need so you can focus on deploying your integration services.
But going beyond that, pretty much each service provided by the major cloud platform such as Azure, AWS, or GCP follows the same principle. Most of them (messaging, machine learning, storage, and so on) abstract all the infrastructure underlying it so you can focus on the real service.
Going back to the Kubernetes ecosystem we have two different layers of that approach. The main one is the managed Kubernetes services that all big platforms provide where all the management of the Kubernetes (master nodes, internal Kubernetes components) are transparent to you and you center everything on the workers. And the second level is what you can get in the AWS world with the EKS + Fargate kind of architecture where not even the worker nodes exist, you have your pods that will be deployed on a machine that belongs to your cluster but you don’t need to worry about it, or manage anything related to that.
So as we have seen serverless approach is coming to all areas but this is not the scope of this article. The idea here is to try to focus on the serverless as a synonym of Function as a Service and (FaaS) and How we can bring the FaaS experience to our productive K8S ecosystem. But let’s start with the initial questions:
Why would we like to do that?
This is the most exciting thing to ask: what are the benefits this approach provides? Function as a Service follows the zero-scale approach. That means that the function is not loaded if they are not being executed, and this is important, especially when you are responsible for your infrastructure or at least paying for it.
Imagine a normal microservices written in any technology, the amount of resources it can use depends on its load, but even without any load, you need some resources to keep it running; mainly, we are talking about memory that you need to stay in use. The actual amount will depend on the technology and the development itself, but it can be moved from some MB to some hundreds. If we consider all the microservices a significant enterprise can get, you will get a difference of several GB that you are paying for that are not providing any value.
But beyond the infrastructure management, this approach also plays very well with another of the latest architectural approaches, the Event-Driven Application (EDA), because we can have services that are asleep just waiting for the right event to wake them up and start processing.
So, in a nutshell, the serverless approach helps you get your optimized infrastructure dream and enable different patterns also in an efficient way. But what happens is I already own the infrastructure? It will be the same because you will run more services in the same infrastructure, so you will still get the optimized use of your current infrastructure.
What do we need to enable that?
The first thing that we need to know is that not all technologies or frameworks are suitable to run on this approach. That is because you need to meet some requirements to be able to do that as a successful approach, as shown below:
- Quick Startup: If your logic is not loaded before a request hits the service, you will need to make sure the logic can load quickly to avoid impacting the consumer of the service. So that means that you will need a technology that can load in a small amount of time, usually talking in the microsecond range.
- Stateless: As your logic is not going to be loaded in a continuous mode it is not suitable for stateful services.
- Disposability: Similar to the previous point it should be ready for graceful shutdown in a robust way
How do we do that?
Several frameworks allow us to get all those benefits that we can incorporate into our Kubernetes ecosystem, such as the following ones:
- KNative: This is the framework that the CNCF Foundation supports and is being included by default in many Kubernetes distributions such as Red Hat Openshift Platform.
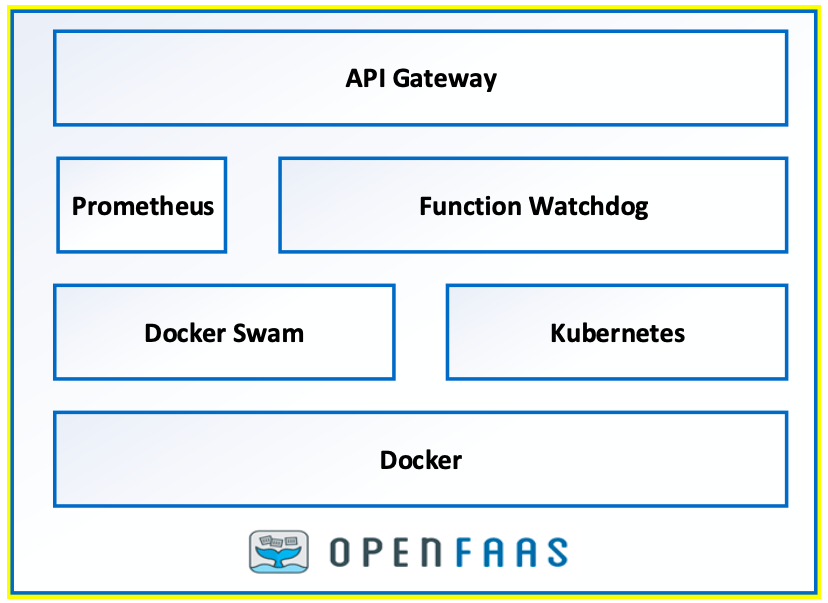
- OpenFaaS: This is a well-used framework created by Alex Ellis that supports the same idea.
It is true that there are other alternatives such as Apache OpenWhisk, Kubeless, or Fission but there less used in today’s world and mainly most alternative has been chosen between OpenFaaS and KNative but if you want to read more about other alternatives I will let you an article about the CNCF covering them so you can take a look for yourself:
📚 Want to dive deeper into Kubernetes? This article is part of our comprehensive Kubernetes Architecture Patterns guide, where you’ll find all fundamental and advanced concepts explained step by step.