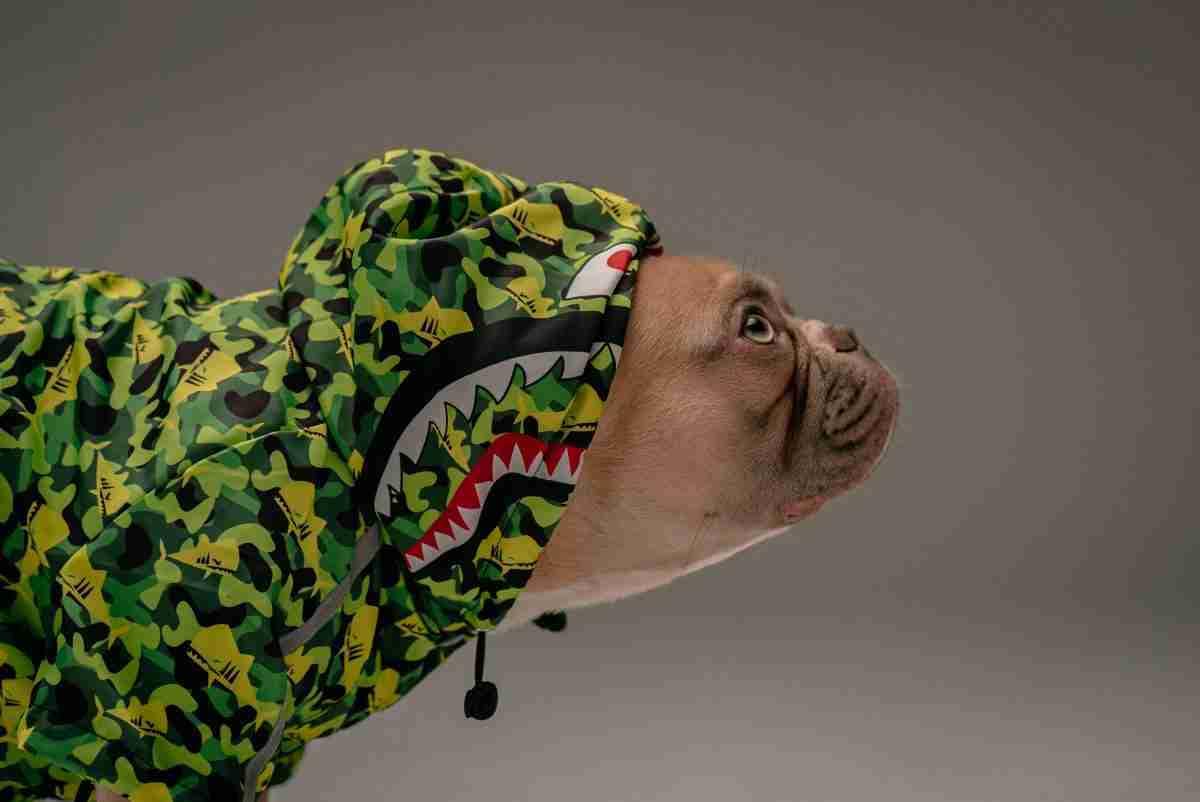
SwaggerUI TIBCO BusinessWorks es una de las características disponibles por defecto para todos los servicios REST de TIBCO BusinessWorks desarrollados. Como probablemente sepas, SwaggerUI es solo una página HTML con una representación gráfica del archivo de definición de Swagger (o especificación OpenAPI para ser más precisos con la versión actual de los estándares en uso) que ayuda a entender la operación y capacidades expuestas por el servicio y también proporciona una manera fácil de probar el servicio como puedes ver en la imagen a continuación:
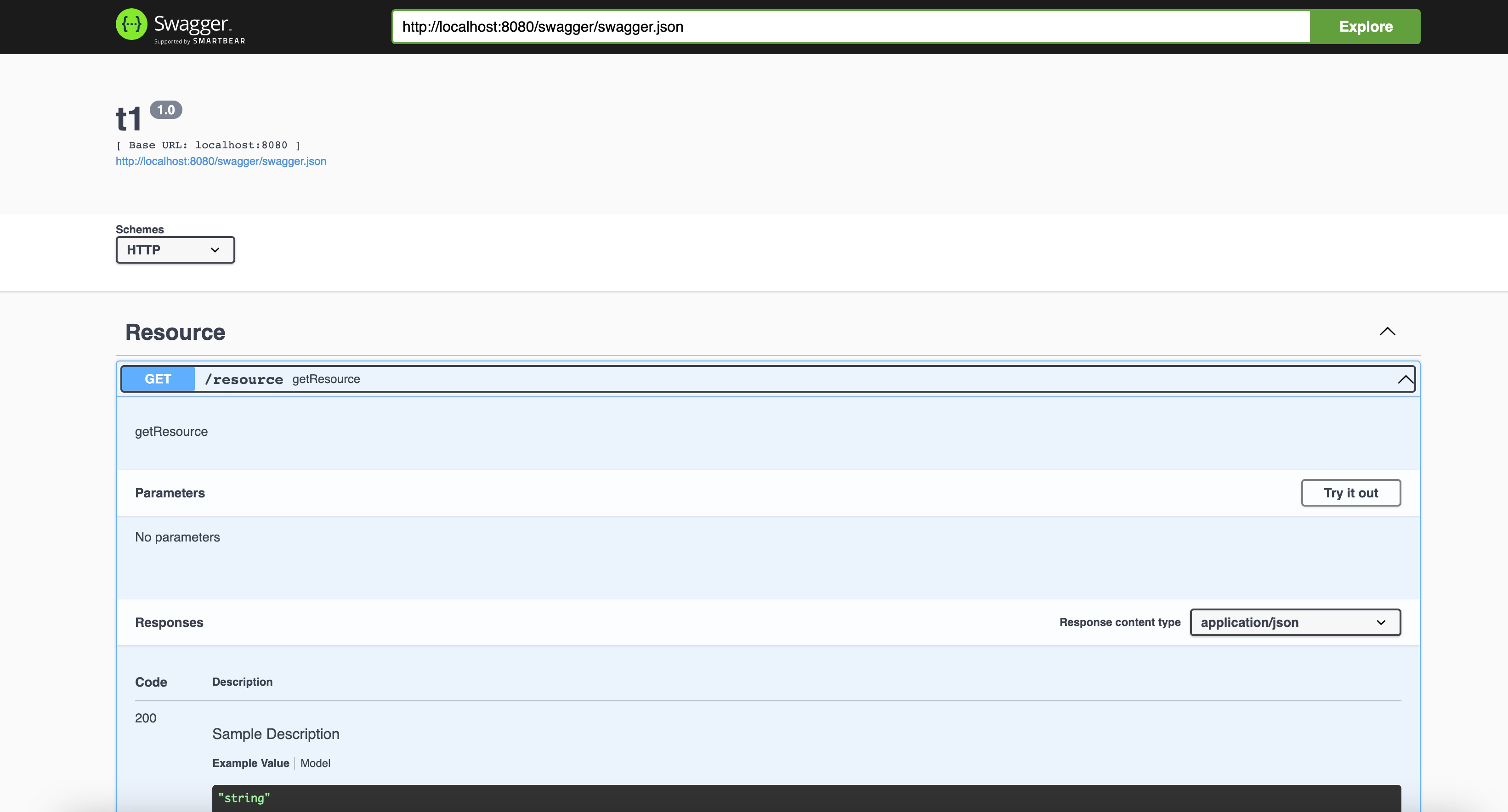
Esta interfaz se proporciona de manera predeterminada para cualquier servicio REST desarrollado usando TIBCO BusinessWorks que utiliza un puerto diferente (7777 por defecto) en caso de que estemos hablando de una implementación local o en el endpoint /swagger en caso de que estemos hablando de una edición de contenedor de TIBCO BusinessWorks.
¿Cómo funciona SwaggerUI para cargar la especificación de Swagger?
SwaggerUI funciona de una manera particular. Cuando llegas a la URL de SwaggerUI, hay otra URL que generalmente es parte de un campo de texto dentro de la página web que contiene el enlace al documento JSON o YAML que almacena la especificación real, como puedes ver en la imagen a continuación:
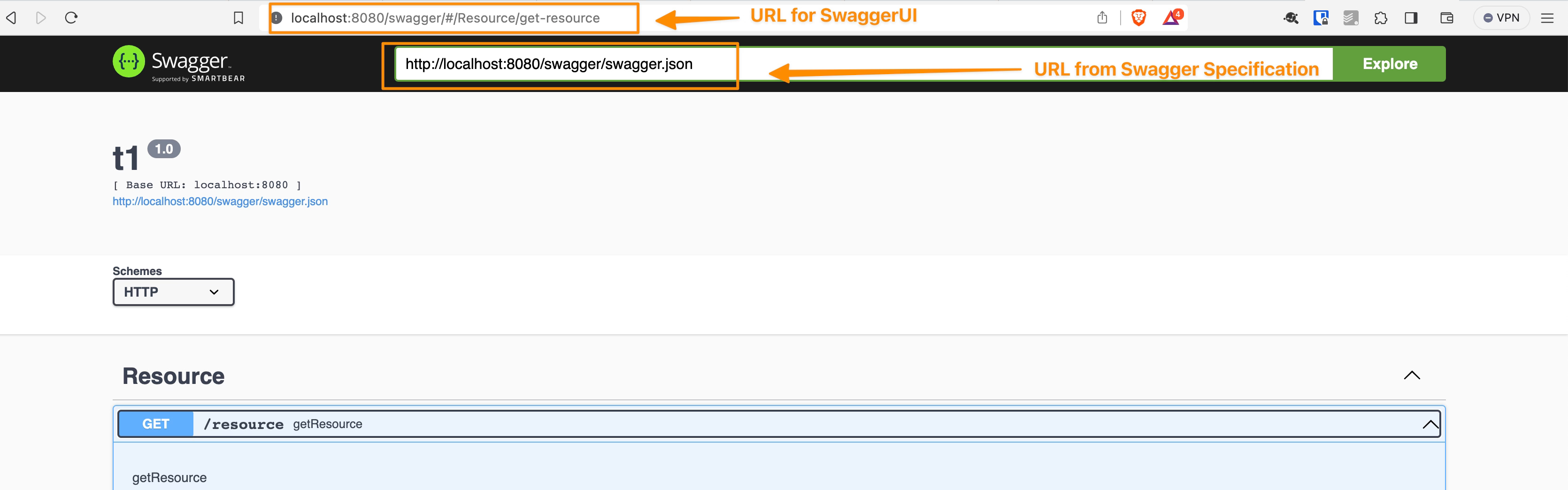
Entonces, puedes pensar que este es un proceso de 2 llamadas:
- La primera llamada carga SwaggerUI como un contenedor gráfico
- Luego, basado en la URL interna proporcionada allí, realiza una segunda llamada para recuperar la especificación del documento
- Y con esa información, renderiza la información en el formato de SwaggerUI.
El problema surge cuando SwaggerUI se expone detrás de un balanceador de carga porque la segunda URL necesita usar la URL anunciada ya que el servidor backend no es alcanzado directamente por el cliente que navega por SwaggerUI. Esto se resuelve de manera predeterminada con las capacidades de Kubernetes en el caso de TIBCO BWCE, y para la implementación local, ofrece dos propiedades para manejar eso de la siguiente manera:
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Sección: Configuración de Swagger REST de BW. Las propiedades en esta sección
# son aplicables al marco de Swagger que es utilizado por el enlace REST de BW.
#
# Nota: Hay propiedades adicionales de configuración de Swagger REST de BW que
# se pueden especificar en el archivo de configuración de BW AppNode "config.ini". Consulta
# la sección "Configuración de Swagger REST de BW" del archivo de configuración de BW AppNode
# para más detalles.
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Nombre de host del proxy inverso del marco de Swagger. Esta propiedad es opcional y
# especifica el nombre de host del proxy inverso en el que el marco de Swagger sirve
# los API's, el endpoint de documentación, api-docs, etc.
bw.rest.docApi.reverseProxy.hostName=localhost
# Puerto del marco de Swagger. Esta propiedad es opcional y especifica el
# puerto del proxy inverso en el que el marco de Swagger sirve los API's, el endpoint de documentación,
# api-docs, etc.
bw.rest.docApi.reverseProxy.port=0000
Puedes navegar por la página de documentación oficial para obtener información más detallada.
Eso resuelve el problema principal con respecto al nombre de host y el puerto que debe ser alcanzado como lo requiere el usuario final. Aún así, hay un componente pendiente en la URL que podría generar un problema, y ese es el protocolo, así que, en resumen, si esto se expone usando HTTP o HTTPS.
¿Cómo manejar la URL de Swagger al descargar SSL?
Hasta el lanzamiento de TIBCO BWCE 2.8.3, el protocolo dependía de la configuración del conector HTTP que usabas para exponer el componente swagger. Entonces, si usas un conector HTTP sin configuración SSL, intentará alcanzar el endpoint usando una conexión HTTP. En el otro caso, si usas un conector HTTP con una conexión SSL, intentará usar una conexión HTTPS. Eso parece bien, pero algunos casos de uso podrían generar un problema:
Certificado SSL descargado en el balanceador de carga: Si descargamos la configuración SSL en el balanceador de carga como se usa en implementaciones tradicionales locales y algunas de las configuraciones de Kubernetes, el consumidor establecerá una conexión HTTPS con el balanceador de carga, pero internamente la comunicación con el BWCE se realizará usando HTTP, por lo que, en este caso, generará una discrepancia, porque en la segunda llamada de las solicitudes adivinará que como el conector HTTP de BWCE no está usando HTTPS, la URL debería ser alcanzada usando HTTP pero ese no es el caso ya que la comunicación pasa por el balanceador de carga que maneja la seguridad.
Exposición de servicio de malla de servicios: Similar al caso anterior, pero en ese caso, cerca de la implementación de Kubernetes. Supongamos que estamos usando malla de servicios como Istio u otros. En ese caso, la seguridad es una de las cosas que necesita ser manejada. Por lo tanto, la situación es la misma que el escenario anterior porque el BWCE no conoce la configuración de seguridad pero está impactando el endpoint predeterminado generado.
¿Cómo habilitar SwaggerUI TIBCO BusinessWorks al descargar certificados SSL?
Desde BWCE 2.8.3, hay una nueva propiedad JVM que podemos usar para forzar que el endpoint generado sea HTTPS incluso si el conector HTTP utilizado por la aplicación BWCE no tiene ninguna configuración de seguridad que nos ayude a resolver este problema en los casos anteriores y en un escenario similar. La propiedad se puede agregar como cualquier otra propiedad JVM usando la propiedad de entorno BW_JAVA_OPTS, y el valor es este: bw.rest.enable.secure.swagger.url =true

