Introducción
Este artículo tiene como objetivo mostrar la Configuración de TIBCO BW Hashicorp Vault para integrar su aplicación TIBCO BW con los secretos almacenados en Hashicorp Vault, principalmente para la externalización y gestión de recursos de contraseñas y credenciales.
Como probablemente sepa, en la aplicación TIBCO BW, la configuración se almacena en Propiedades a diferentes niveles (propiedades de Módulo o Aplicación). Puede leer más sobre ellas aquí. Y el propósito principal de esas propiedades es proporcionar flexibilidad a la configuración de la aplicación.
Estas propiedades pueden ser de diferentes tipos, como String, Integer, Long, Double, Boolean y DateTime, entre otros recursos técnicos dentro de TIBCO BW, como se muestra en la imagen a continuación:
La integración de TIBCO BW Hashicorp Vault afectará solo a aquellas propiedades de tipo Contraseña (al menos hasta la versión 2.7.2/6.8.1 de BW). La razón detrás de esto es que esas propiedades son el tipo de datos relevantes para la información que es sensible y necesita ser segura. Otros conceptos pueden ser gestionados a través de componentes estándar de Kubernetes como ConfigMaps.
Definición de la Aplicación BW
Vamos a comenzar con una aplicación sencilla, como puede ver en la imagen a continuación:
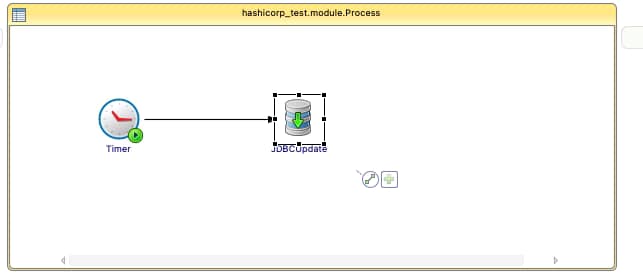
Solo un temporizador simple que se ejecutará una vez e insertará la hora actual en la base de datos PostgreSQL. Usaremos Hashicorp Vault para almacenar la contraseña del usuario de la base de datos para poder conectarnos a ella. El nombre de usuario y la cadena de conexión residirán en un ConfigMap.
Omitiremos la parte de la configuración relacionada con el despliegue de los Contenedores de la aplicación TIBCO BW y enlazaremos a un ConfigMap. Tiene un artículo que cubre eso en detalle en caso de que necesite seguirlo, y nos centraremos solo en el tema relacionado con la integración de TIBCO BW Hashicorp Vault.
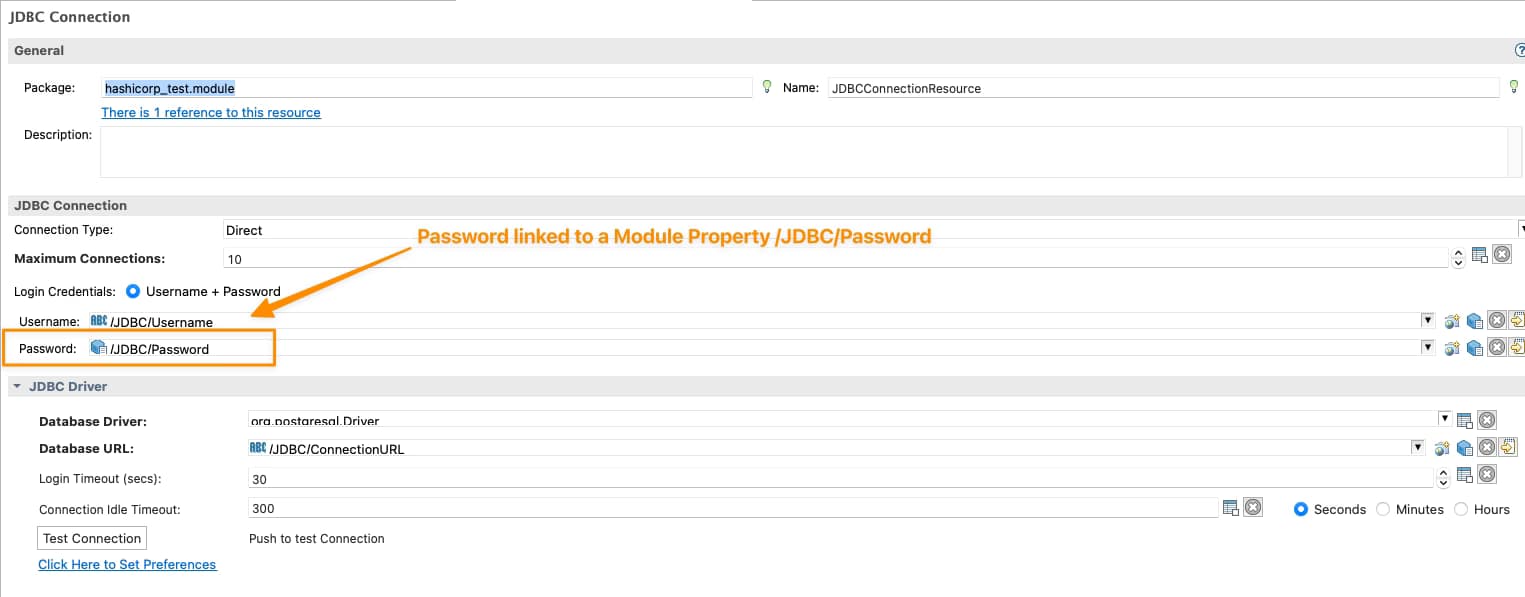
Así que necesitaremos decirle a TIBCO BW que la contraseña del Recurso Compartido JDBC estará vinculada a la configuración de Hashicorp Vault, y para hacer eso, lo primero es haber vinculado la Contraseña de los Recursos Compartidos a una Propiedad de Módulo como se muestra en la imagen a continuación:
Ahora, necesitamos decirle a esta Propiedad de Módulo que está vinculada a Hashicorp Vault, y lo haremos en la Vista de Propiedades de la Aplicación, seleccionando que esta propiedad está vinculada a una Solución de Gestión de Credenciales como se muestra en la imagen a continuación:
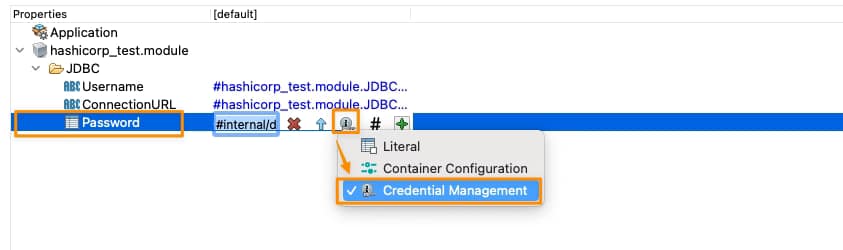
Y es ahora cuando establecemos la relación de TIBCO BW Hashicorp Vault. Necesitamos hacer clic directamente en el signo más verde, y tendremos una ventana modal que nos pedirá la tecnología de gestión de credenciales que vamos a usar y los datos necesarios para cada una de ellas, como puede ver en la siguiente imagen:
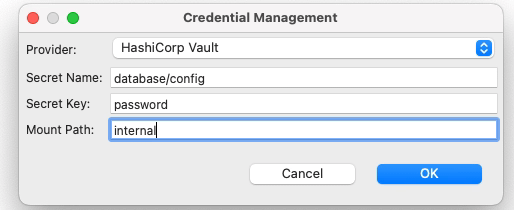
Seleccionaremos Hashicorp Vault como el proveedor. Luego necesitaremos proporcionar tres atributos que ya comentamos en el artículo anterior cuando comenzamos a crear secretos en Hashicorp Vault:
- Nombre del Secreto: este es el nombre del secreto después de la ruta raíz del elemento.
- Clave del Secreto: Esta es la clave dentro del propio secreto
- Ruta de Montaje: Esta es la ruta raíz del secreto
Para obtener más detalles sobre estos tres conceptos, por favor, consulte nuestro artículo sobre cómo crear secretos en Hashicorp Vault.
Así que con todo esto, tenemos prácticamente todo lo que necesitamos para conectarnos a Hashicorp Vault y obtener el secreto, y desde el lado de TIBCO BW BusinessStudio, todo está hecho; podemos generar el archivo EAR y desplegarlo en Kubernetes porque aquí está la última parte de nuestra configuración.
Despliegue en Kubernetes
Hasta este momento, ya hemos proporcionado la siguiente información:
- Proceso BW que tiene el inicio de sesión para conectarse a la Base de Datos e insertar información
- Enlace entre la propiedad de contraseña utilizada para conectar y la definición del Secreto de Hashicorp
Así que, prácticamente todo está ahí, pero falta un concepto. ¿Cómo se conectará el Pod de Kubernetes a Hashicorp una vez que el pod esté desplegado? Hasta este punto, no proporcionamos la ubicación del servidor de Hashicorp Vault del método de autenticación para conectarse a él. Esta es la parte que falta de la integración de TIBCO BW Hashicorp Vault y será parte del archivo YAML de Despliegue de Kubernetes.
Lo haremos usando las siguientes propiedades de entorno en este ejemplo:
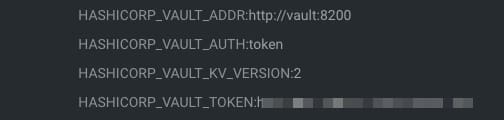
- HASHICORP_VAULT_ADDR: Esta variable apuntará a donde se encuentra el servidor de Hashicorp Vault
- HASHICORP_VAULT_AUTH: Esta variable indicará qué opciones de autenticación se utilizarán. En nuestro caso, usaremos la de token como usamos en el artículo anterior
- HASHICORP_VAULT_KV_VERSION: Esta variable indica qué versión de la solución de almacenamiento KV estamos usando y será dos por defecto.
- HASHICORP_VAULT_TOKEN: Este será solo el valor del token para poder autenticarse contra el servidor de Hashicorp Vault
Si está utilizando otros métodos de autenticación o simplemente quiere saber más sobre esas propiedades, por favor, eche un vistazo a esta documentación de TIBCO.
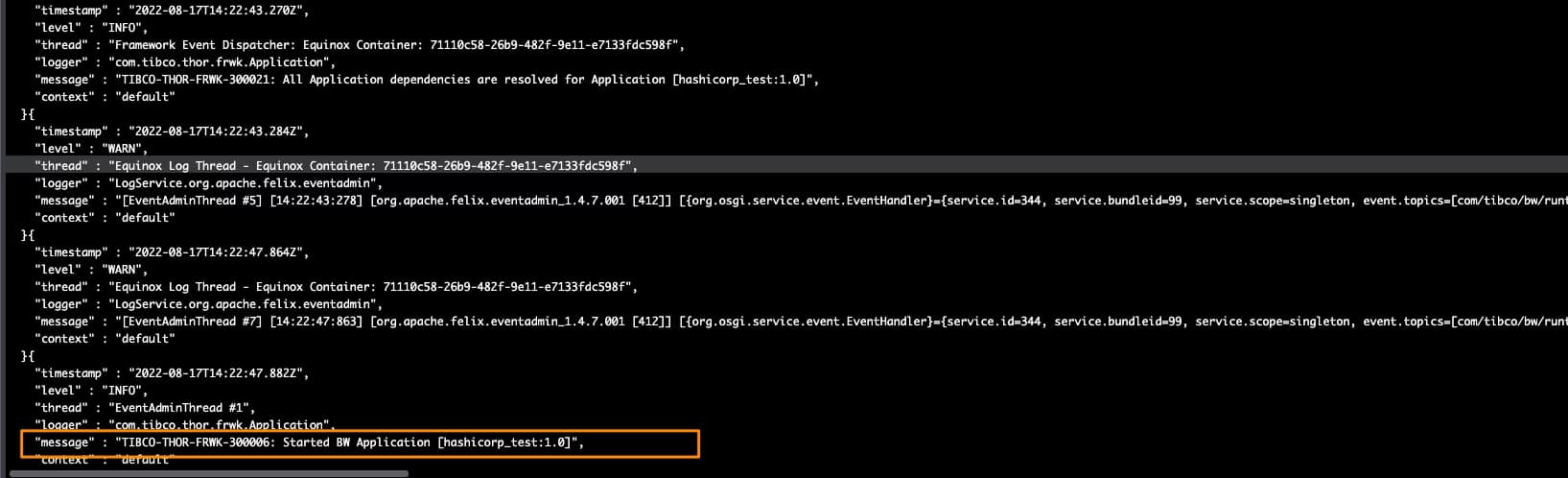
Con todo eso agregado a las propiedades de entorno de nuestra aplicación TIBCO BW, podemos ejecutarla, y obtendremos una salida similar a esta, que muestra que la integración de TIBCO BW Hashicorp Vault se ha realizado y la aplicación pudo iniciarse sin ningún problema