Background: MinIO and the Maintenance Mode announcement
MinIO has long been one of the most popular self-hosted S3-compatible object storage solutions for Kubernetes, especially for logs, backups, and internal object storage in on‑premise and cloud-native environments. Its simplicity, performance, and API compatibility made it a common default choice for backups, artifacts, logs, and internal object storage.
In late 2025, MinIO marked its upstream repository as Maintenance Mode and clarified that the Community Edition would be distributed source-only, without official pre-built binaries or container images. This move triggered renewed discussion across the industry about sustainability, governance, and the risks of relying on a single-vendor-controlled “open core” storage layer.
A detailed industry analysis of this shift, including its broader ecosystem impact, can be found in this InfoQ article
—
What exactly changed?
1. Maintenance Mode
Maintenance Mode means:
- No new features
- No roadmap-driven improvements
- Limited fixes, typically only for critical issues
- No active review of community pull requests
As highlighted by InfoQ, this effectively freezes MinIO Community as a stable but stagnant codebase, pushing innovation and evolution exclusively toward the commercial offerings.
2. Source-only distribution
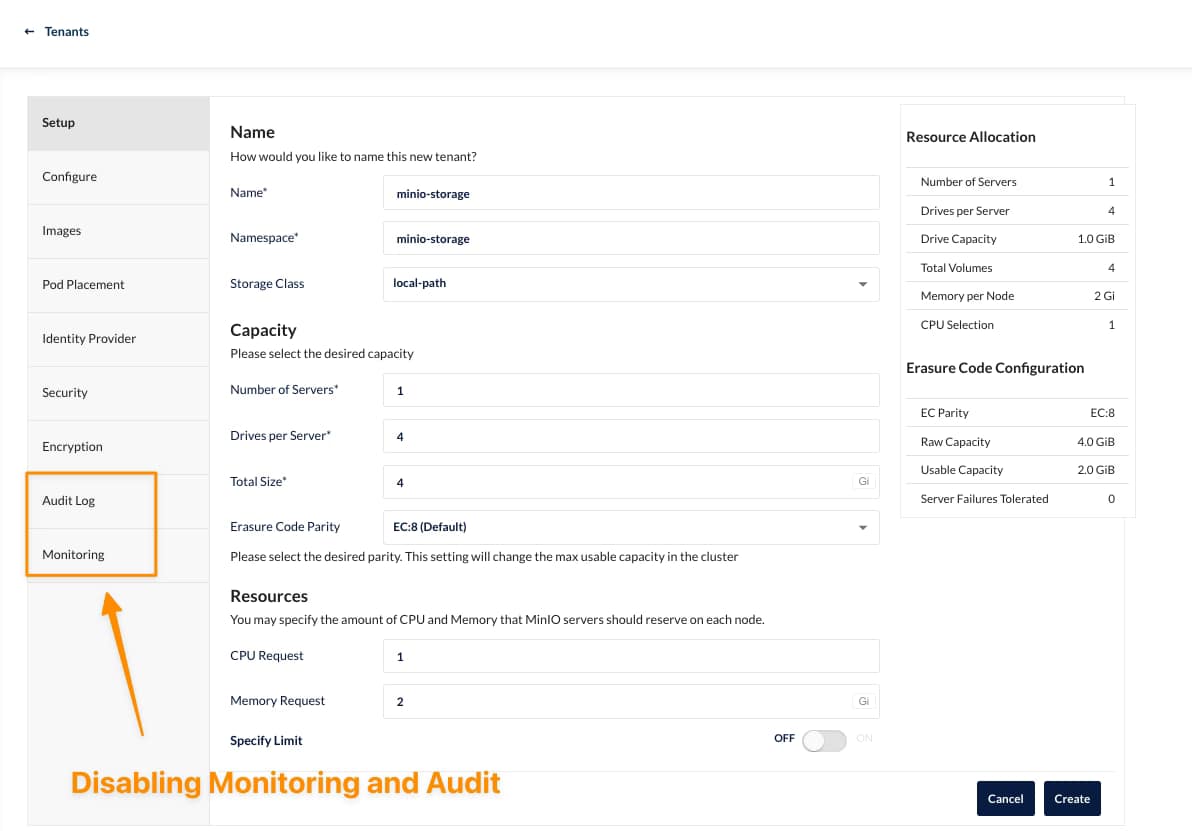
Official binaries and container images are no longer published for the Community Edition. Users must:
- Build MinIO from source
- Maintain their own container images
- Handle signing, scanning, and provenance themselves
This aligns with a broader industry pattern noted by InfoQ: infrastructure projects increasingly shifting operational burden back to users unless they adopt paid tiers.
—
Direct implications for Community users
Security and patching
With no active upstream development:
- Vulnerability response times may increase
- Users must monitor security advisories independently
- Regulated environments may find Community harder to justify
InfoQ emphasizes that this does not make MinIO insecure by default, but it changes the shared-responsibility model significantly.
Operational overhead
Teams now need to:
- Pin commits or tags explicitly
- Build and test their own releases
- Maintain CI pipelines for a core storage dependency
This is a non-trivial cost for what was previously perceived as a “drop‑in” component.
Support and roadmap
The strategic message is clear: active development, roadmap influence, and predictable maintenance live behind the commercial subscription.
—
Impact on OEM and embedded use cases
The InfoQ analysis draws an important distinction between API consumers and technology embedders.
Using MinIO as an external S3 service
If your application simply consumes an S3 endpoint:
- The impact is moderate
- Migration is largely operational
- Application code usually remains unchanged
Embedding or redistributing MinIO
If your product:
- Ships MinIO internally
- Builds gateways or features on MinIO internals
- Depends on MinIO-specific operational tooling
Then the impact is high:
- You inherit maintenance and security responsibility
- Long-term internal forking becomes likely
- Licensing (AGPL) implications must be reassessed carefully
For OEM vendors, this often forces a strategic re-evaluation rather than a tactical upgrade.
—
Forks and community reactions
At the time of writing:
- Several community forks focus on preserving the MinIO Console / UI experience
- No widely adopted, full replacement fork of the MinIO server exists
- Community discussion, as summarized by InfoQ, reflects caution rather than rapid consolidation
The absence of a strong server-side fork suggests that most organizations are choosing migration over replacement-by-fork.
—
Best S3-Compatible Alternatives to MinIO: Ceph RGW, SeaweedFS, Garage
InfoQ highlights that the industry response is not about finding a single “new MinIO”, but about selecting storage systems whose governance and maintenance models better match long-term needs.
Ceph RGW
Best for: Enterprise-grade, highly available environments
Strengths: Mature ecosystem, large community, strong governance
Trade-offs: Operational complexity
SeaweedFS
Best for: Teams seeking simplicity and permissive licensing
Strengths: Apache-2.0 license, active development, integrated S3 API
Trade-offs: Partial S3 compatibility for advanced edge cases
Garage
Best for: Self-hosted and geo-distributed systems
Strengths: Resilience-first design, active open-source development
Trade-offs: AGPL license considerations
Zenko / CloudServer
Best for: Multi-cloud and Scality-aligned architectures
Strengths: Open-source S3 API implementation
Trade-offs: Different architectural assumptions than MinIO
—
Recommended strategies by scenario
If you need to reduce risk immediately
- Freeze your current MinIO version
- Build, scan, and sign your own images
- Define and rehearse a migration path
If you operate Kubernetes on-prem with HA requirements
- Ceph RGW is often the most future-proof option
If licensing flexibility is critical
- Start evaluation with SeaweedFS
If operational UX matters
- Shift toward automation-first workflows
- Treat UI forks as secondary tooling, not core infrastructure
—
Conclusion
MinIO’s shift of the Community Edition into Maintenance Mode is less about short-term breakage and more about long-term sustainability and control.
As the InfoQ analysis makes clear, the real risk is not technical incompatibility but governance misalignment. Organizations that treat object storage as critical infrastructure should favor solutions with transparent roadmaps, active communities, and predictable maintenance models.
For many teams, this moment serves as a natural inflection point: either commit to self-maintaining MinIO, move to a commercially supported path, or migrate to a fully open-source alternative designed for the long run.
📚 Want to dive deeper into Kubernetes? This article is part of our , where you’ll find all fundamental and advanced concepts explained step by step.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does Maintenance Mode mean for MinIO Community Edition?
Maintenance Mode for MinIO Community Edition means the upstream codebase is effectively frozen. There will be no new features, only critical bug fixes, and community pull requests will not be actively reviewed. Furthermore, official pre-built binaries and container images are no longer provided; users must build from source.
Is MinIO Community Edition still safe to use?
The code itself isn’t inherently insecure, but the shared-responsibility model changes. Security patching for non-critical issues will be slower or non-existent. For production, especially in regulated environments, you must now actively monitor advisories and maintain your own built and scanned images, which increases operational risk.
What is the best open-source alternative to MinIO for Kubernetes?
The best alternative depends on your needs. For enterprise-grade, high-availability setups, Ceph RGW is the most robust choice. For simplicity and Apache 2.0 licensing, SeaweedFS is excellent. For geo-distributed, resilience-first designs, evaluate Garage. There is no direct drop-in replacement; each requires evaluation.
Should I fork MinIO or migrate to another solution?
For most organizations, migration is preferable to forking. Maintaining a full fork of a complex storage server involves significant long-term commitment to security, bug fixes, and potential feature backporting. The industry trend, as noted, is toward migration to systems with active upstream development and clear governance.
How does this affect products that embed MinIO (OEM use)?
The impact on OEMs is high. You inherit full maintenance and security responsibility. Long-term internal forking becomes likely, and the AGPL licensing implications must be carefully reassessed. This often forces a strategic re-evaluation of your embedded storage layer rather than a simple tactical update.