Introduction
This article aims to show the TIBCO BW Hashicorp Vault Configuration to integrate your TIBCO BW application with the secrets stored in Hashicorp Vault, mainly for the externalization and management of password and credentials resources.
This article is part of my comprehensive TIBCO Integration Platform Guide where you can find more patterns and best practices for TIBCO integration platforms.
As you probably know, in the TIBCO BW application, the configuration is stored in Properties at different levels (Module or Application properties). You can read more about them here. And the primary purpose of that properties is to provide flexibility to the application configuration.
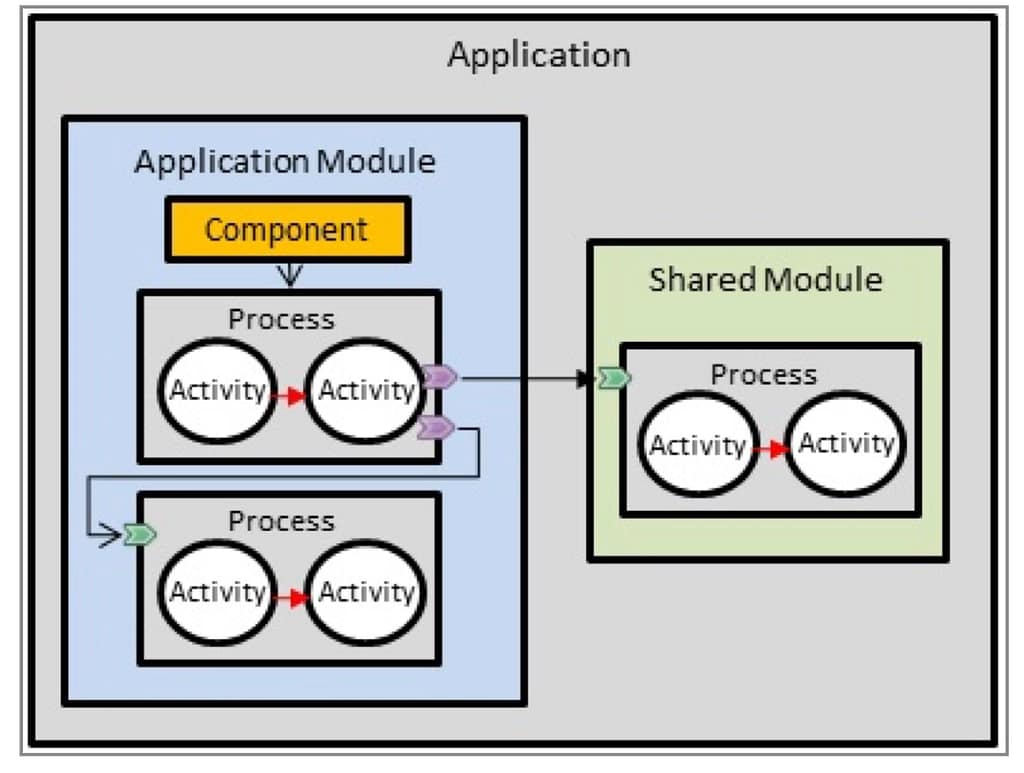
These properties can be of different types, such as String, Integer, Long, Double, Boolean, and DateTime, among other technical resources inside TIBCO BW, as shown in the picture below:
The TIBCO BW Hashicorp Vault integration will affect only those properties of Password type (at least up to 2.7.2/6.8.1 BW version). The reason behind that is that those properties are the kind of data relevant to the information that is sensitive and needs to be secure. Other concepts can be managed through standard Kubernetes components such as ConfigMaps.
BW Application Definition
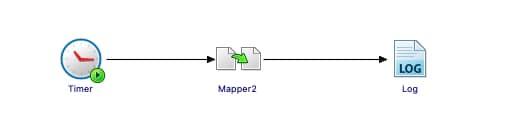
We are going to start with a straightforward application, as you can see in the picture below:
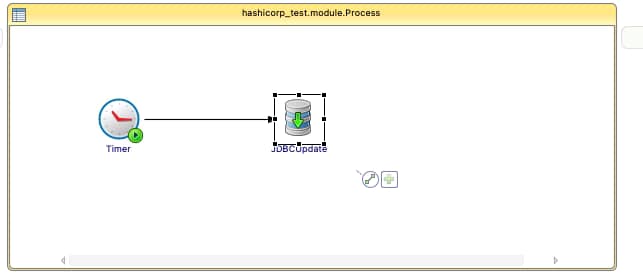
Just a simple timer that will be executed once and insert the current time into the PostgreSQL database. We will use Hashicorp Vault to store the password of the database user to be able to connect to it. The username and the connection string will reside on a ConfigMap.
We will skip the part of the configuration regarding the deployment of the TIBCO BW application Containers and link to a ConfigMap you have an article covering that in detail in case you need to follow it, and we will focus just on the topic regarding TIBCO BW Hashicorp Vault integration.
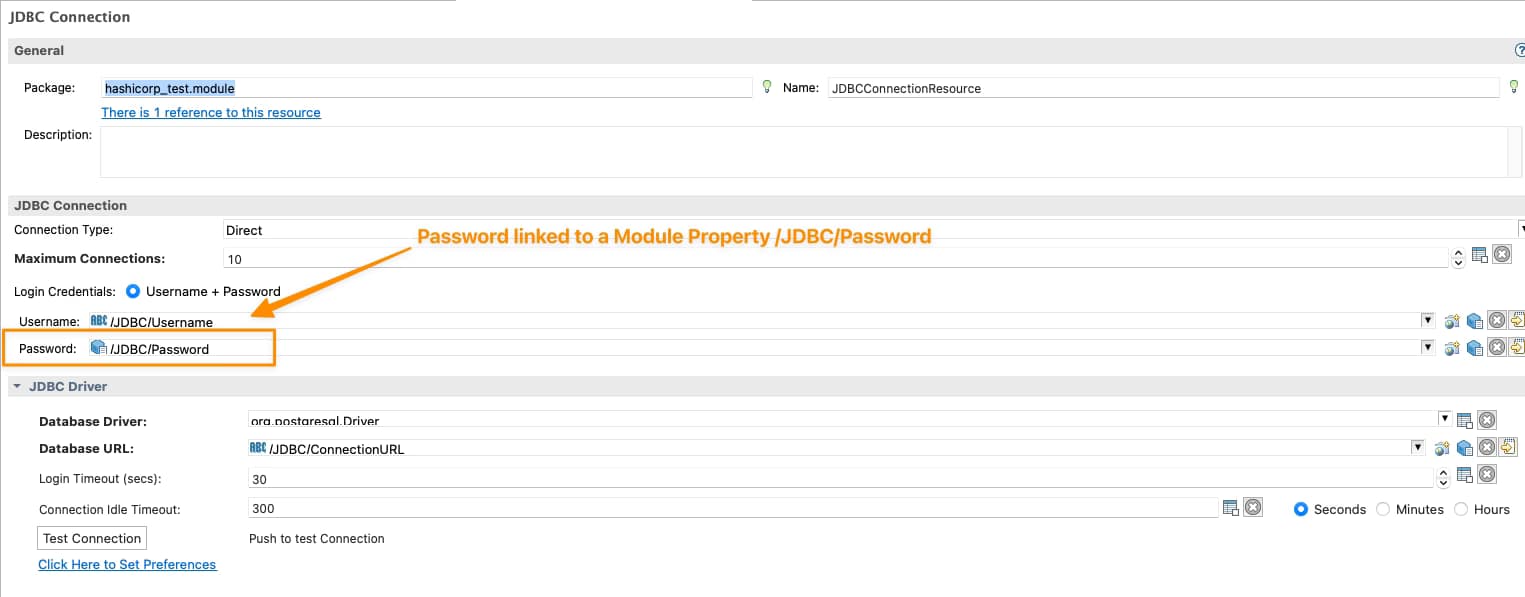
So we will need to tell TIBCO BW that the password of the JDBC Shared Resource will be linked to Hashicorp Vault configuration, and to do that, the first thing is to have tied the Password of the Shared Resources to a Module Property as shown in the picture below:
Now, we need to tell this Module Property that is Linked to Hashicorp Vault, and we will do that on the Application Property View, selecting that this property is linked to a Credential Management Solution as shown in the picture below:
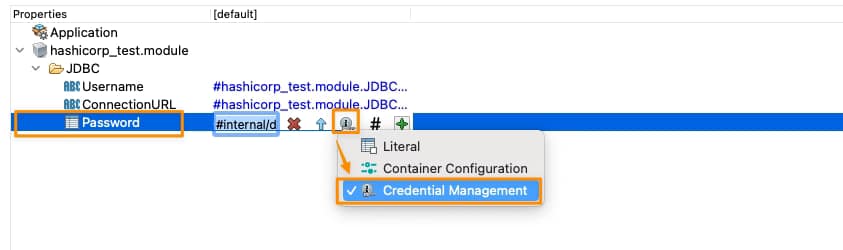
And it is now when we establish the TIBCO BW Hashicorp Vault relationship. We need to click directly on the green plus sign, and we will have a modal window asking for the technology of credentials management that we’re going to use and the data needed for each of them, as you can see in the following picture:
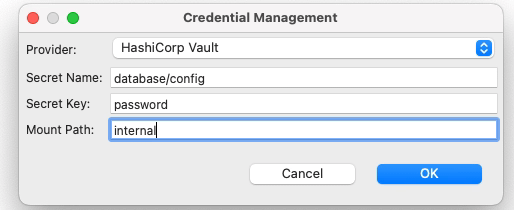
We will select Hashicorp Vault as the provided. Then we will need to provide three attributes that we already commented on in the previous article when we start creating secrets in Hashicorp Vault:
- Secret Name: this is the secret name path after the root path of the element.
- Secret Key: This is the key inside the secret itself
- Mount Path: This is the root path of the secret
To get more details about these three concepts, please look at our article about how to create secrets in Hashicorp Vault.
So with all this, we have pretty much everything we need to connect to Hashicorp Vault and grab the secret, and from the TIBCO BW BusinessStudio side, everything is done; we can generate the EAR file and deploy it into Kubernetes because here it is the last part of our configuration.
Kubernetes Deployment
Until this moment, we have the following information already provided:
- BW Process that has the login to connect to the Database and insert information
- Link between the password property used to connect and the Hashicorp Secret definition
So, pretty much everything is there, but one concept is missing. How will the Kubernetes Pod connect to Hashicorp once the pod is deployed? Until this point, we didn’t provide the Hashicorp Vault server location of the authentication method to connect to it. This is the missing part of the TIBCO BW Hashicorp Vault integration and will be part of the Kubernetes Deployment YAML file.
We will do that using the following environment properties in this sample:
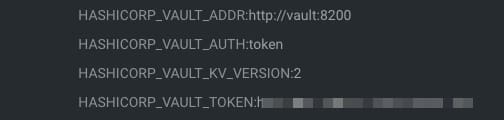
- HASHICORP_VAULT_ADDR: This variable will point to where the Hashicorp Vault server is located
- HASHICORP_VAULT_AUTH: This variable will indicate which authentication options will be used. In our case, we will use the token one as we used in the previous article
- HASHICORP_VAULT_KV_VERSION: This variable indicates which version of the KV storage solution we are using and will be two by default.
- HASHICORP_VAULT_TOKEN: This will be just the token value to be able to authentication against the Hashicorp Vault server
If you are using other authentication methods or just want to know more about those properties please take a look at this documentation from TIBCO.
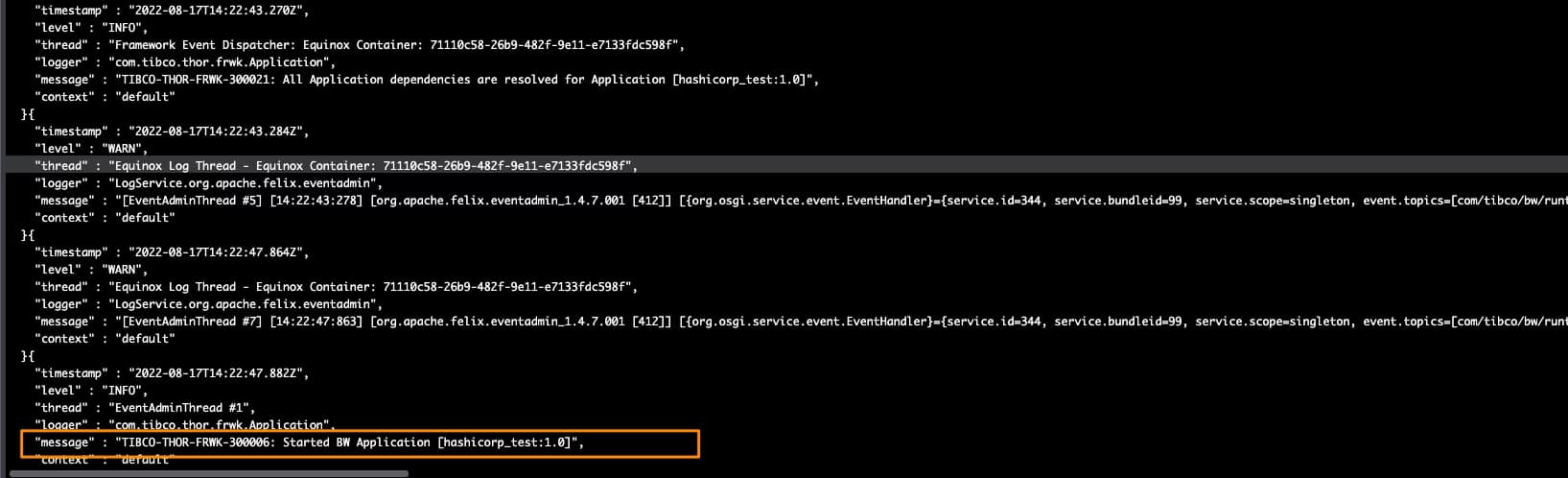
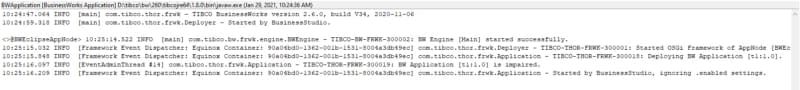
With all that added to the environment properties of our TIBCO BW application, we can run it, and we will get an output similar to this one, and that shows that the TIBCO BW Hashicorp Vault integration has been done and the application was able to start without any issue