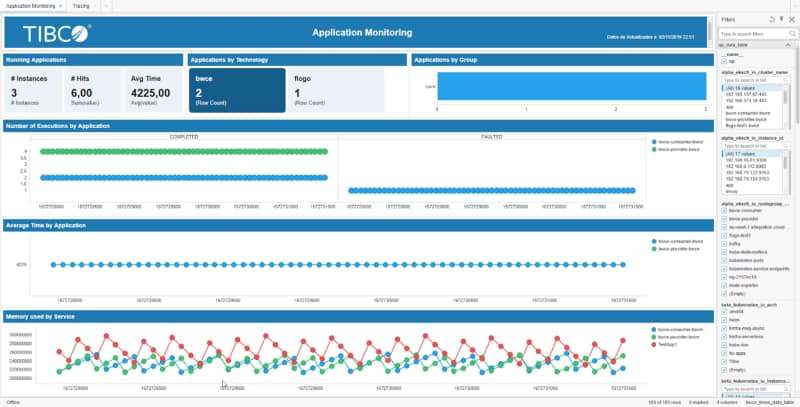
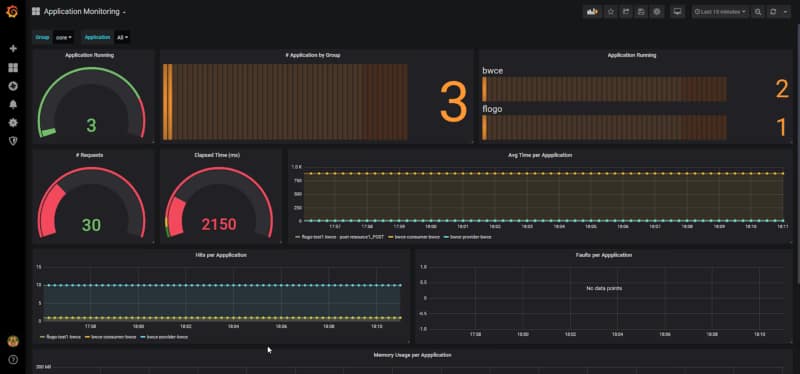
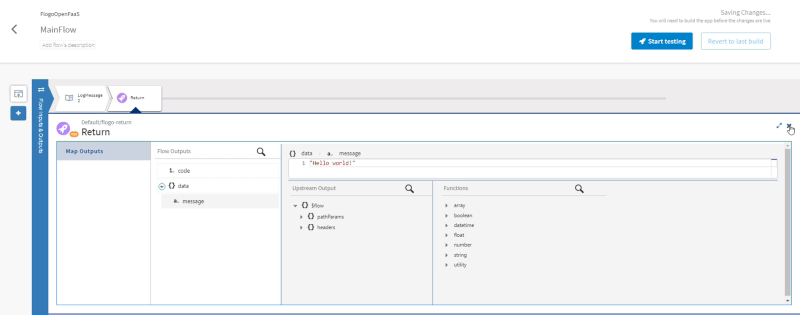
Provide more agility to your troubleshooting efforts by debugging exactly where the error is happening using Remote Debugging techniques

Container revolution has provided a lot of benefits, as we have been discussed in-depth in other articles, and at the same time, it has also provided some new challenges that we need to tackle.
This article is part of my comprehensive TIBCO Integration Platform Guide where you can find more patterns and best practices for TIBCO integration platforms.
All agility that we have now in the hands of our developers needs to be also extended to the maintenance work and fixing things. We need to be agile as well. We know some of the main issues that we have regarding this: It works on my environment, with the data set that I have, I couldn’t see the issue, or I couldn’t reproduce the error, are just sentences that we listen to over and over and delay the resolution of some errors or improvements even when the solution is simple we struggle in getting a real scenario to test.
And here is where Remote Debugging comes in. Remote Debugging is, just as its own name clearly states, to be able to debug something that is not local that is remote. It has been focused since its conception in Mobile Development because it doesn’t matter how good the simulator is. You will always need to test in a real device to make sure everything is working properly.
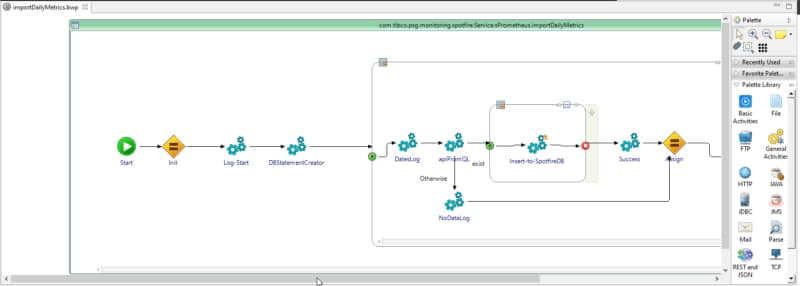
So this is the same concept but applicable to a container, so that means that I have a TIBCO BusinessWorks application running on Kubernetes. We want to debug it as it has been running locally, as shown in the image before. To be able to do that, we need to follow these steps:
Enabling the Remote Debugging in the pod
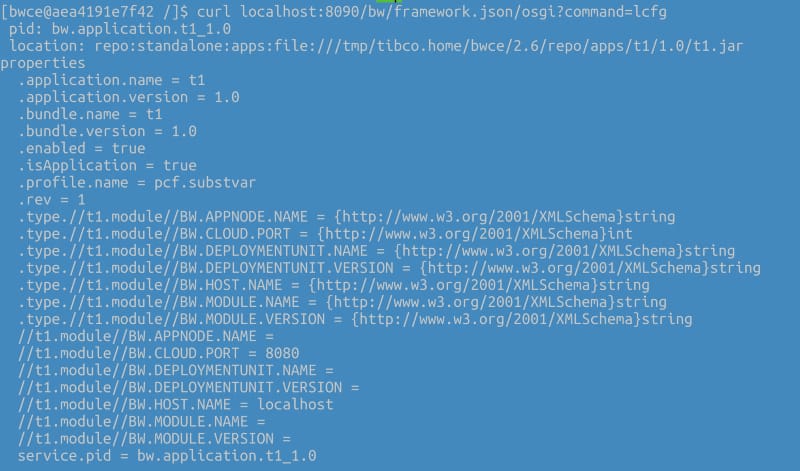
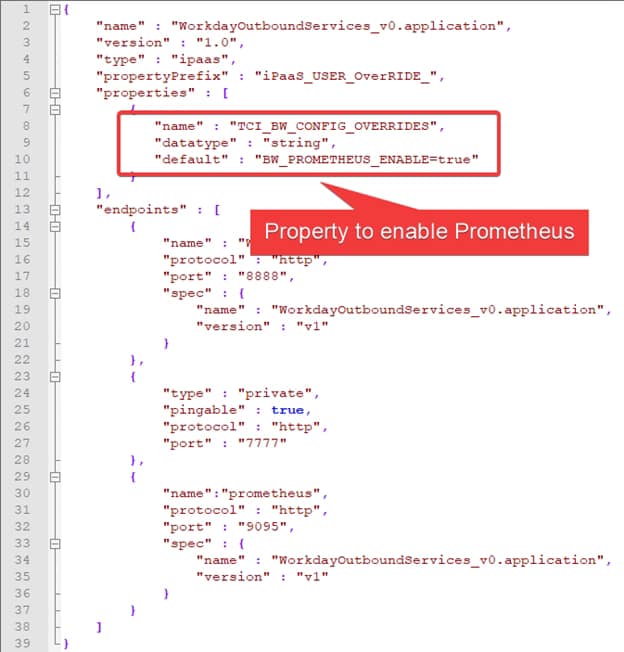
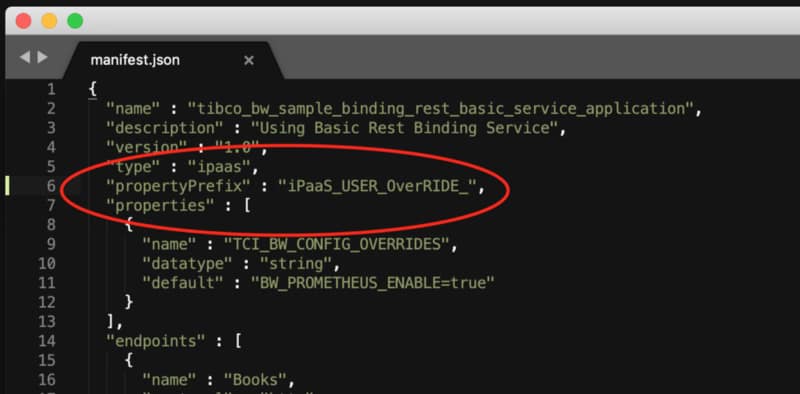
The first step is to enable the remote debug option in the application and to do that, we need to use the internal API that the BusinessWorks provides, and to do that, we need to execute from inside the container:
curl -XPOST http://localhost:8090/bw/bwengine.json/debug/?interface=0.0.0.0&port=5554&engineName=Main
In case that we do not have any tool like curl or wget to hit a URL inside the container, you can always use the port-forward strategy to make the 8090 port from the pod accessible to enable the debug port using a command similar to the one below:
kubectl port-forward hello-world-test-78b6f9b4b-25hss 8090:8090
And then, we can hit it from our local machine to enable remote debugging
Make the Debug Port accessible to the Studio
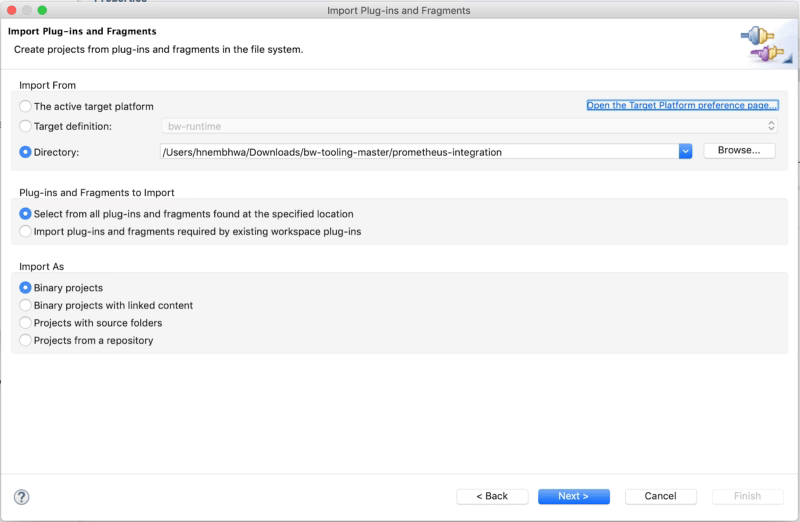
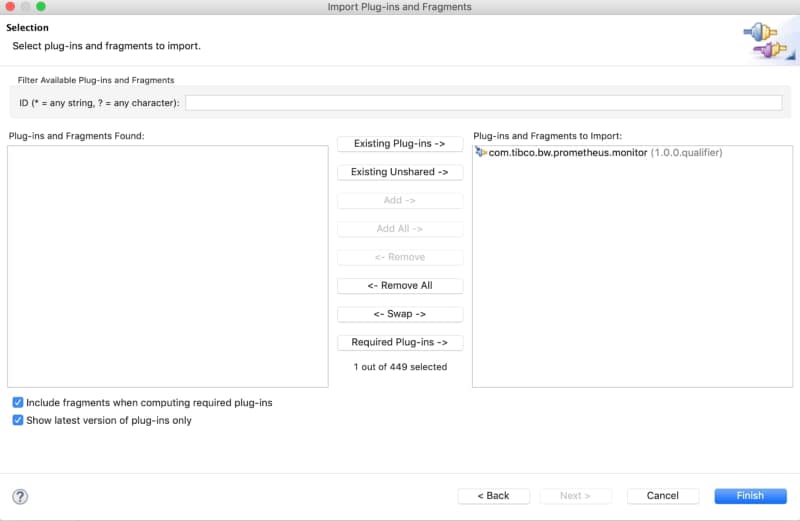
To do the remote debugging, we need to be able to connect our local TIBCO BusinessStudio to this specific pod that is executing the load and, to do that, we need to have access to the Debug port. To get this, we have mainly two options that are the ones shown in the subsections below: Expose the port at the pod level and port-forwarding option.
Expose the port at the Pod Level
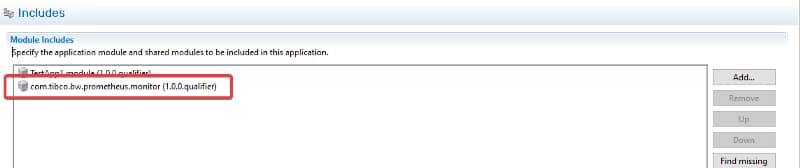
We need to have the debug port opened in our pod. To do that, we need to define another port that is not in use by the application, and it is not the default administration port (8090) to the one to be exposed. For example, in my case, I will use 5554 as the debug port, and to do that, I define another port to be accessed.
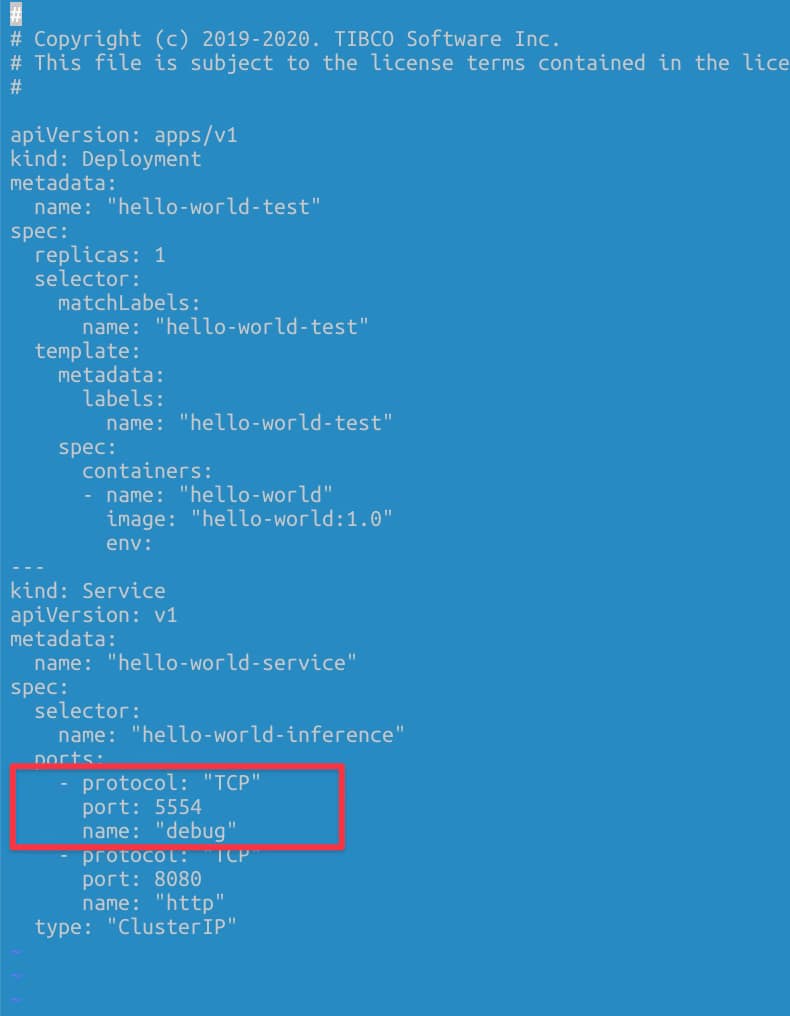
Port-Forwarding Option
Another option if we do not want to expose the debug port all the time, even if this is not going to be used unless we’re executing the remote debug, we have another option to do a port-forward to the debug port in our local.
kubectl port-forward hello-world-test-78b6f9b4b-cctgh 5554:5554
Connection to the TIBCO Business Studio
Now that we have everything ready, we need to connect our local TIBCO Business Studio to the pod, and to do that, we need to follow these steps:
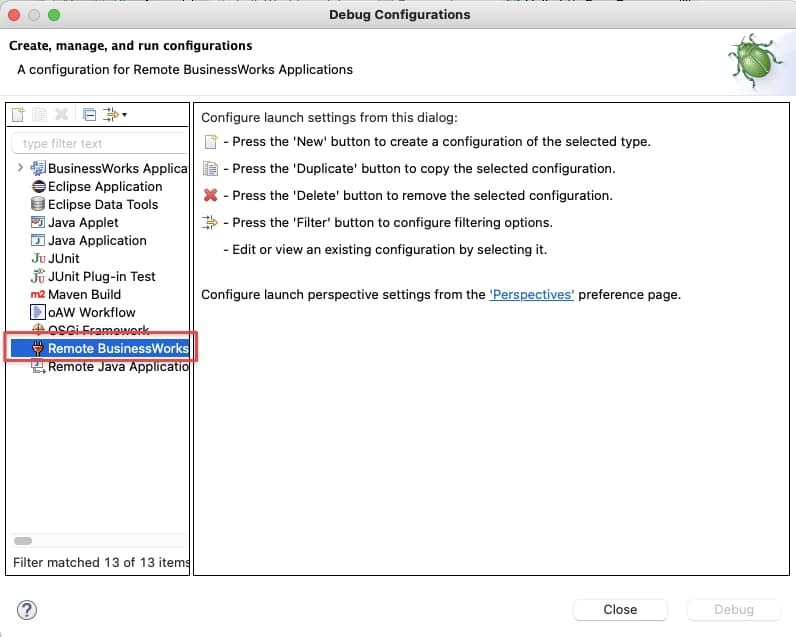
Run → Debug Configurations, and we select the Remote BusinessWorks
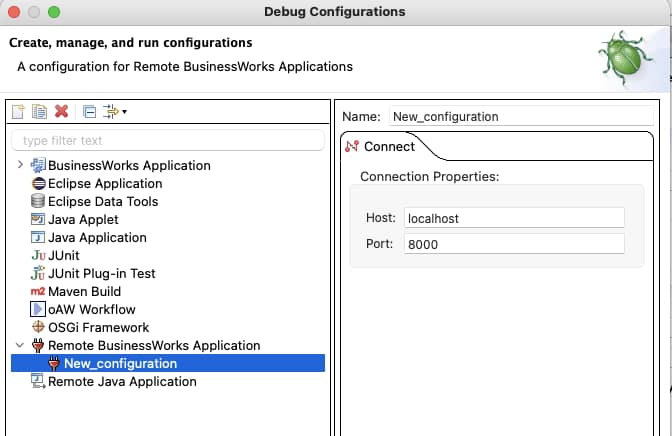
And now we need to provide the connection details. For this case, we will use the localhost and port 5554 and click on the Debug button.
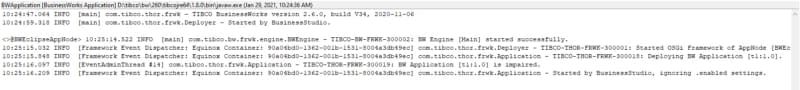
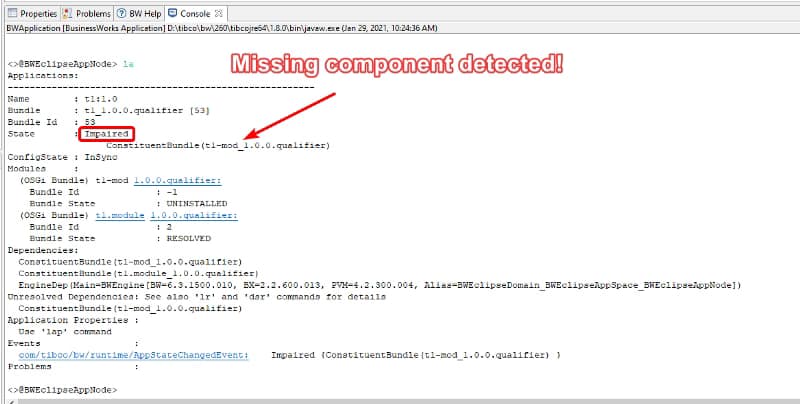
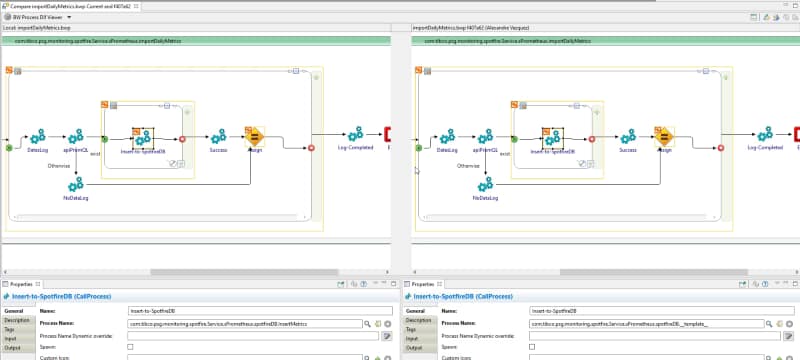
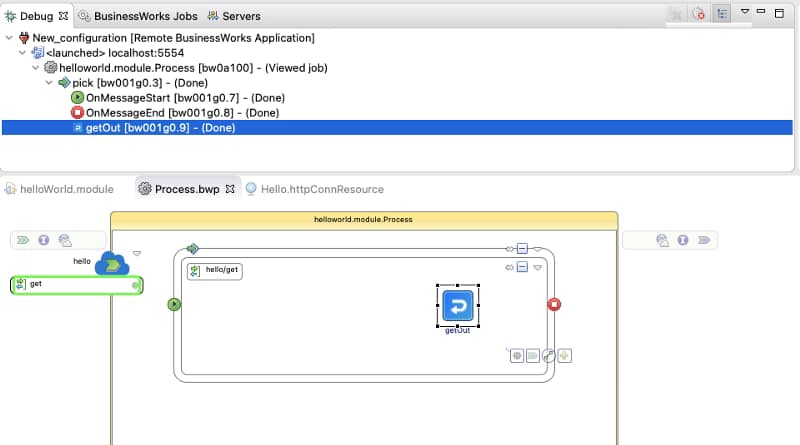
After that moment, we will establish a connection between both environments: the pod running on our Kubernetes cluster and our local TIBCO BusinessStudio. And as soon as we hit the container, we can see the execution in our local environment:
Summary
I hope you find this interesting, and if you are one of those facing this issue now, you have information not to be stopped by this one. If you would like to submit your questions feel free to use one of the following options:
- Twitter: You can send me a mention at @alexandrev on Twitter or a DM or even just using the hashtag #TIBFAQS that I will monitor.
- Email: You can send me an email to alexandre.vazquez at gmail.com with your question.
- Instagram: You can send me a DM on Instagram at @alexandrev